Have you ever heard that “we are what we eat”? And this reality has somehow been forgotten in this fast-paced era. Still, we can not deny the facts. Our bodies work like a fine-tuned machine, and the best fuel can only help our bodies keep moving with energy. Your family relations, work life, mood, and overall health depend on which nutrients you feed your body.

You have noticed that often, some days, you get up with full energy, while other days feel a bit off, though you have taken the same hours of sleep. This is because of what your body is consuming in the form of food. A balanced diet with the right amount of nutrients not only acts as the best fuel for the body but also boosts your mood. In this article, we will talk about the 10 essential nutrients your body needs for your optimal health, energy, and happier days.
Carbohydrates: Body’s primary source of energy
Carbohydrates, often called carbs, are the primary source of your body’s energy, though they have a bad reputation. The key is choosing the whole and unprocessed carbohydrates in the diet, which improve your health and give energy rather than crashing it.

Animal-based sources:
- Dairy: Milk, yogurt, cheese, and honey.
Plant-based sources:
- Grains: Whole-wheat bread, whole-wheat pasta, quinoa, oatmeal, and brown rice.
- Fruits: Bananas, apples, berries, mangoes, melons, and oranges.
- Vegetables: Beetroots, sweet potatoes, potatoes, and peas.
- Legumes: Lentils, red kidney beans, chickpeas, and black beans.
- Proteins: Body’s strength and repair
Proteins are the main nutrients for your body’s well-being. They are the essential source of your muscles’ strength and hormonal balance.
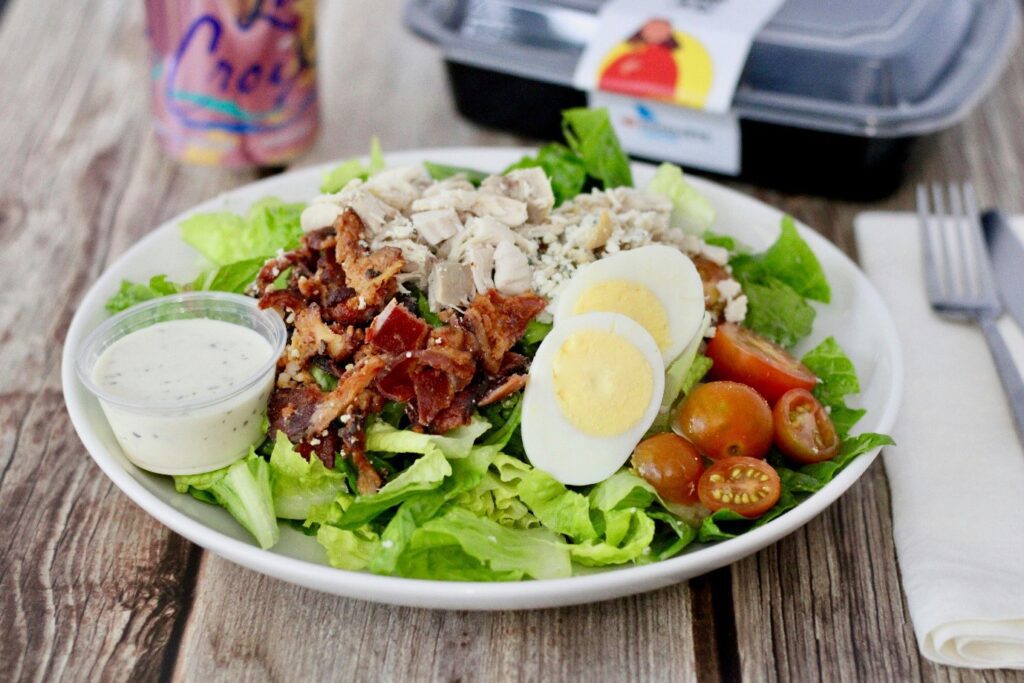

Animal-based sources:
- Lean meat: Chicken, beef, mutton, and turkey.
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and low-fat cottage cheese.
- Seafood: Fishes and shellfish.
Plant-based sources:
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas.
- Soy products: Tofu
- Nuts: Walnuts, almonds, and peanuts.
- Seeds: Sunflower seeds.
- Grains:
Healthy Fats: The Brain’s fuel and hormone balance
Not all fats are bad fats; some fats, like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated (omega-3 and omega-6) fats, are crucial for your brain health, heart functioning, and hormone balance. Only limiting saturated fats and avoiding trans fats is recommended.
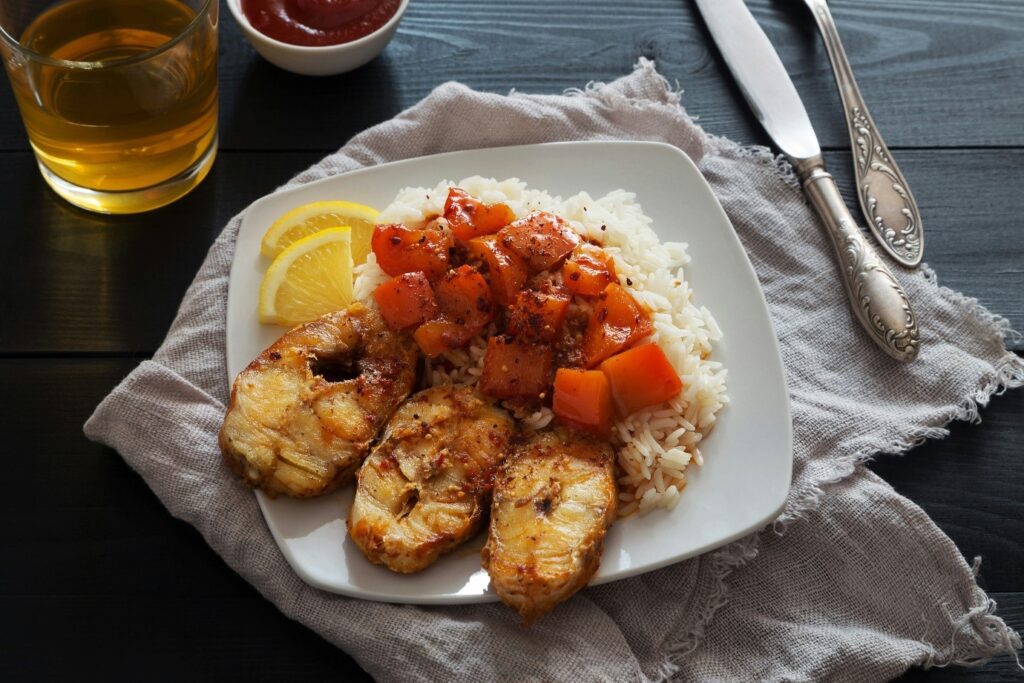

Monounsaturated fats (MUFAs)
Animal-based sources:
- Meat: Red meats.
- Dairy: Whole milk products.
Plant-based sources:
- Fruits:
- Oils: Olive oil, canola oil, sesame oil, safflower oil, and peanut oil.
- Seeds and Nuts: Hazelnuts, cashews, almonds, macadamia nuts, and pistachios.
Polyunsaturated fats (PUFAs)
Animal-based sources:
- Seafood: Mussels and scallops.
- Fish: Trout, salmon, mackerel, herring, and sardines.
Plant-based sources:
- Oils: Grapeseed oil, flaxseed oil, sunflower oil, soybean oil, safflower oil, canola oil.
- Seeds: Flax seeds, chia seeds, and sunflower seeds.
- Nuts:
- Other: Tofu and avocados.
- Vitamins: Body’s immune booster
Vitamins are the essential organic nutrients. Your body does not produce them in sufficient amounts, so they are taken through the diet. Vitamins play a crucial role in cell metabolism, physiological processes, and immune functioning. Out of 13 essential vitamins which your body needs, some are fat-soluble (A, D, E, and K) and others are water-soluble (C and 8 types of vitamin B).
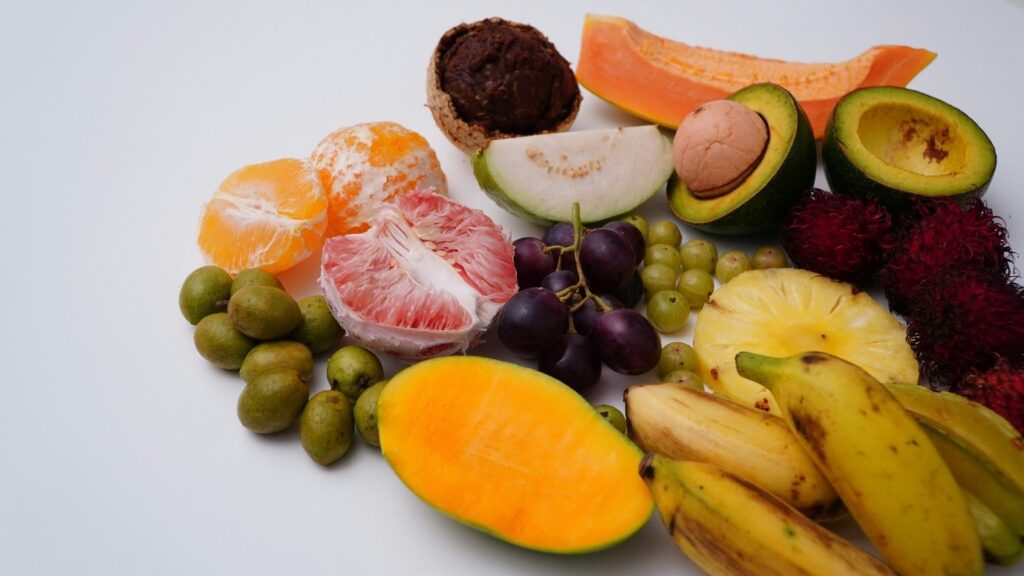

Animal-based sources:
- A: Fortified dairy products, milk, cheese, eggs, and liver.
- B12: Milk, cheese, eggs, fish, poultry, and meat.
- D: Fortified dairy products, egg yolk, and fatty fish.
- K: Milk and eggs.
- B (B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6): Milk, poultry, meat, eggs, and fish.
Plant-based sources:
- A: Leafy green vegetables, spinach, kale, sweet potatoes, carrots, and mangoes.
- C: Strawberries, berries, potatoes, bell peppers, broccoli, and citrus fruits.
- D: Mushrooms.
- E: Leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.
- K: Kale, spinach, leafy green vegetables, broccoli, and cabbage.
- B (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9 – Folate): Fortified cereals, whole grains, asparagus, nuts, seeds, and legumes (lentils, peas, beans).
Minerals: Body’s silent support system
Minerals are crucial for your muscle strength, strong bones, and steady nerves. These are essential inorganic nutrients that are obtained from the diet. They are categorised as macro minerals (calcium, magnesium, potassium, sulphur, chloride, sodium, and phosphorus), required in larger amounts, i.e., over 200mg daily, and trace minerals (zinc, selenium, manganese, copper, iodine, and iron), required in smaller amounts.
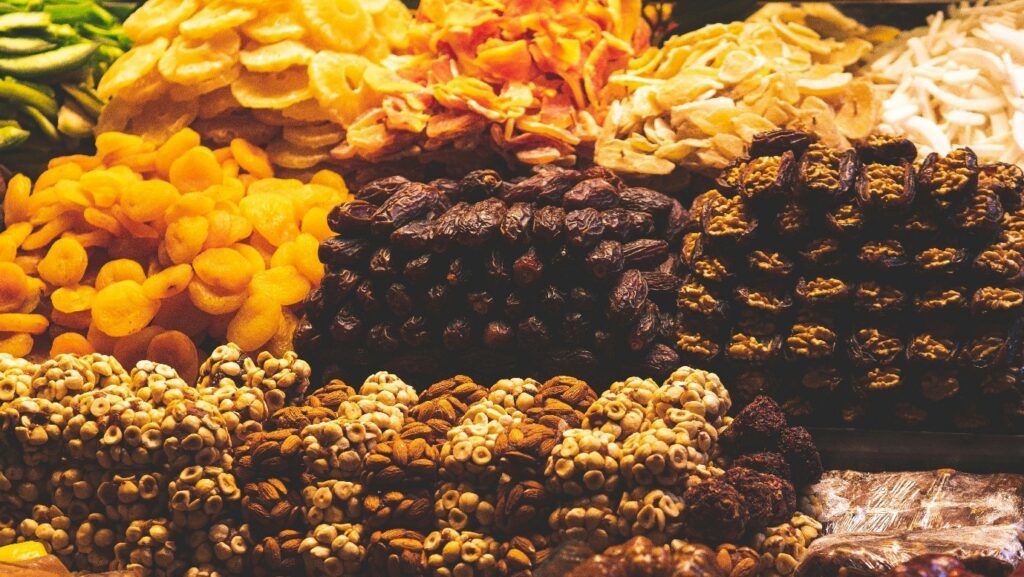

Animal-based sources:
- Dairy products: Calcium and phosphorus.
- Eggs: Iron, zinc, selenium, and phosphorus.
- Meat: Iron, phosphorus, and zinc.
- Seafood: Selenium, zinc, and iodine.
Plant-based sources:
- Whole Grains: Iron, zinc, magnesium, and phosphorus.
- Vegetables: Potassium, iron, magnesium, and calcium.
- Seeds and Nuts: Zinc, iron, selenium, magnesium, and calcium.
- Legumes: Zinc, magnesium, iron, and phosphorus.
- Fruits: Magnesium and potassium.
Water: Body’s overlooked nutrient
Water – an essential nutrient – makes up 60% of your body mass. It plays a vital role in every function of the body, including the transport of oxygen and nutrients, the regulation of body temperature, the lubrication of joints, and the elimination of waste.

Sources:
Your body’s water needs can be fulfilled by drinking plain water available. Some fruits and vegetables, like cucumbers, celery, watermelons, and oranges, also have high water content.
Fiber: Best friend of the body’s digestive system
Fiber is the most important component of a healthy diet. It is critical for your overall health and various body functions, which include regulating your food digestion, maintaining a healthy microbiome in the gut, reducing cholesterol, and controlling blood sugar levels. Fiber is a plant-based nutrient.

Plant-based sources:
- Vegetables: Leafy green vegetables, brussels sprouts, sweet potatoes, broccoli, carrots, and artichokes.
- Fruits: Oranges, avocados, bananas, pears, berries, and apples.
- Grains: Oats, barley, whole grain cereals, quinoa, brown rice, and whole-wheat bread.
- Legumes: Lentils, peas, beans, and other pulses.
- Seeds and Nuts: Almonds, sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, and chia seeds.
- Others: Dark chocolate, baked potatoes, and popcorn.
Antioxidants: Body’s stress defenders
The unstable molecules called free radicals cause cellular damage while antioxidants protect your body from these free radicals. Many antioxidants are naturally produced by your body, while dietary antioxidants are obtained from vegetables, fruits, nuts, and whole grains.
Dietary antioxidants reduce the risk of various diseases, maintain physiological functions, and also reduce your body’s stress. Dietary antioxidants include vitamins (A, C, and E), carotenoids (provitamin A), anthocyanins, allium sulphur, flavonoids, and polyphenols.

Animal-based sources:
- Eggs and dairy products.
- Poultry and meats.
Plant-based sources:
- Vegetables and Fruits: Leafy green vegetables, eggplant, tomatoes, citrus fruits, berries, and grapes.
- Seeds and Nuts.
- Other plant sources: Dark chocolate, herbs, green tea, cocoa, and spices.
Probiotics: Gut and immune system friendly
Probiotics are the living microorganisms, also called “good” bacteria and yeast. They are your gut’s best friend. They not only support gut health but also boost your immune system by balancing the microbiome of your body. They are naturally present in your digestive system and also taken through diet and supplements.

Animal-based sources:
- Kefir: Fermented milk drink.
- Yogurt
- Cheese
- Buttermilk
Plant-based sources:
- Fermented Vegetables: Kimchi, sauerkraut, and pickles.
- Fermented Legumes and Grains: Miso, sourdough bread, tempeh.
- Fermented Beverages: Water kefir and kombucha.
- Yogurts: Coconut, almond, and soy milk yogurts.
Phytochemicals: Body’s secret healer
Phytochemicals are not considered essential nutrients as they are not crucial for the physiological functioning of your body. But they offer potential health benefits. They have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Phytochemicals are produced in plants only, but can be obtained from those animals that have consumed the plants and have become part of their bodies.
Animal-based sources:
- Dairy
- Meat
Plant-based sources:
- Vegetables and Fruits: Sweet potatoes, garlic, grapes, apples, berries, and mangoes.
- Grains: Cereals, whole grains, and quinoa.
- Seeds and Nuts.
- Spices and Herbs.
- Beverages: Juices, tea, and coffee.
The key takeaways
- For a healthy body and mind, you need a balanced diet with a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, unsaturated fats, vitamins, fibres, antioxidants, probiotics, and phytochemicals.
- Adding a good portion of vegetables, fruits, and nuts gives your body an ample amount of nutrients.
- Each nutrient has a unique function in your body, so choose your meal thoughtfully.
- Small changes in daily habits, like the replacement of unhealthy and processed snacks with nuts, can make a big difference.
- Lifestyle changes, stress management, regular exercise, and a good night’s sleep are also important for the function of nutrients we take from our diet.
- If your body is getting weak or feeling any unusual symptoms, you can add nutrient supplements to your diet after consulting a nutritionist.
Conclusion
So, at the end of the day, giving priority to your health should not have to be complicated. It is always about making some mindful choices, which start to become your routine over time. A balanced diet, having the right portion of all 10 nutrients, not only boosts your health and energy but also makes you more vibrant and happier. And next time, while filling your plate on the dining table, remember: fuel your body with love and healthy intentions.
To find additional information, visit healthabulous, and read our article on “10 superfoods you’re probably not eating (but should be” and some other related topics to get better knowledge of your body’s needs.
FAQs
What are the most important essential nutrients for our optimal health?
For optimal health, water, carbohydrates, proteins, unsaturated fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals are the most important essential nutrients.
Do we need supplements for essential nutrient intake?
A balanced diet is sufficient to fulfill our body’s needs, but some individuals are recommended to take supplements based on their health condition.
Which foods help me boost my immunity?
Citrus fruits, nuts, fish, and probiotic-rich food help to boost the body’s immune system.
How can my nutrient intake be improved?
Have a balanced diet with all portions (carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals, and vitamins) and varieties of food in the everyday intake.
- Should I consult a nutritionist for a customised diet plan?
Yes, it is highly recommended to consult a nutritionist for a customised diet plan once every 6 months at least.
REFERENCES
- Morris AL, Mohiuddin SS. Biochemistry, Nutrients. [Updated 2023 May 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554545/
- Holesh JE, Aslam S, Martin A. Physiology, Carbohydrates. [Updated 2023 May 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459280/
- LaPelusa A, Kaushik R. Physiology, Proteins. [Updated 2022 Nov 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555990/
- LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. Vitamins. 2021 Jun 10. PMID: 31644195.
- National Research Council (US) Committee on Diet and Health. Diet and Health: Implications for Reducing Chronic Disease Risk. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1989. 13, Minerals. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK218735/
- Mashek DG, Wu C. MUFAs. Adv Nutr. 2015 May 15;6(3):276-7. doi: 10.3945/an.114.005926. PMID: 25979493; PMCID: PMC4424766.
- Mititelu M, Lupuliasa D, Neacșu SM, Olteanu G, Busnatu ȘS, Mihai A, Popovici V, Măru N, Boroghină SC, Mihai S, Ioniță-Mîndrican CB, Scafa-Udriște A. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Human Health: A Key to Modern Nutritional Balance in Association with Polyphenolic Compounds from Food Sources. Foods. 2024 Dec 27;14(1):46. doi: 10.3390/foods14010046. PMID: 39796335; PMCID: PMC11719865.
- Bodke H, Jogdand S. Role of Probiotics in Human Health. Cureus. 2022 Nov 9;14(11):e31313. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31313. PMID: 36514580; PMCID: PMC9733784.
- Yang Y, Ling W. Health Benefits and Future Research of Phytochemicals: A Literature Review. J Nutr. 2025 Jan;155(1):87-101. doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2024.11.007. Epub 2024 Nov 12. PMID: 39536969.