Asthma Treatment: Symptoms, Triggers & Care
Asthma affects the lungs and breathing. Because of the severity of the disorder and the age range of individuals impacted by the condition, it is one of the leading respiratory problems. While the problems associated with the condition may be serious, it is ultimately a lifelong condition that requires awareness and monitoring to keep it under control.
Controlling asthma is a balancing act. On one side of the pendulum, asthma control is good enough that it does not impact daily activities or sleep. On the other side of the pendulum, the control is unreasonable, and breathing problems and asthma symptoms affect sleep, activities, and the overall quality of life. This is why understanding the symptoms and what can trigger poor asthma control is very important.
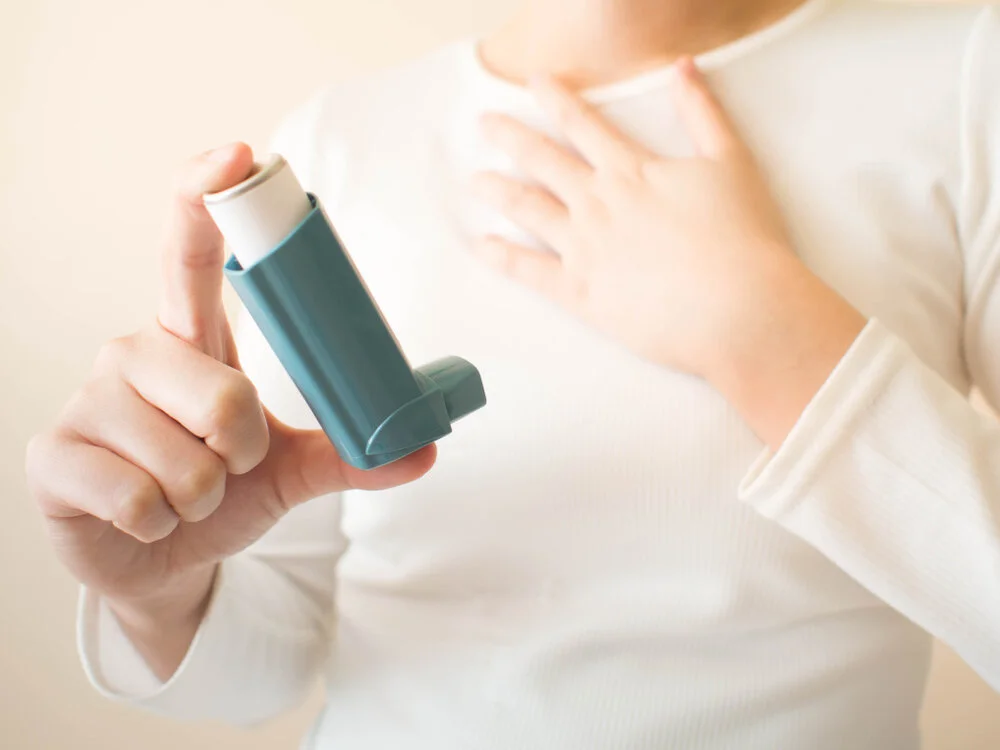

What is Asthma?
Asthma is a condition in which the airways of the lungs become sensitive, inflamed, and narrow, and are triggered by an outside source. There are several external asthma triggers, and when exposed to these, the muscles that surround the inflamed bronchial tubes constrict. The swollen, already irritated lining creates a high level of mucus, which becomes even more constrictive and further impedes airflow.
While infections may cause temporary irritation and breathing problems, asthma is a chronic condition. It is a problem because inflammation is a constant in life and persists even when the symptoms themselves are not active.
Impact of Asthma on the Functionality of the Lungs
Usually, in healthy lungs, the respiratory system takes in oxygen and excretes carbon dioxide without any trouble. However, in people with asthma, the lungs become hyperreactive to specific stimuli, leading to one or more of the following: airway inflammation, bronchial constriction, and mucus hypersecretion.
The aforementioned lung pathologies lead to wheezing, chronic cough, chest constriction, and dyspnea. These symptoms tend to be worse at night or in the early morning.
Various Forms of Asthma
- The various forms of asthma result from patients’ demographic information, their specific triggers, and any other health issues they may face.
- Allergic asthma is most common among individuals with other allergies, such as eczema or allergic rhinitis. It can be triggered by dust, pollen, various types of mould, and animal dander.
- Essentially, non-allergic asthma can be triggered by cold environmental air, highly polluted air, and psychological stress. Also, non-allergic asthma tends to be more common in adults and more challenging to control.
- Asthma triggered by physical exertion is more likely in cold, dry air and is most pronounced during exercise.
- Occupational asthma results from workplace irritants or toxic dust.
Universal Asthma Symptoms
Asthma symptoms tend to be highly variable in both frequency and severity. Some chronic asthmatics may see symptoms disrupt their daily activities, and other people may only have their symptoms occur infrequently.
Symptoms of asthma can vary in severity and include wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, and severe coughing, predominantly nocturnal and early-morning coughing.
Symptoms of asthma can worsen during asthma attacks, which can be severe and life-threatening and are always an emergency. Asthma symptoms can vary from person to person and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during exercise or at night
- Wheezing (a whistling sound when breathing)
- Chest tightness or pain
- Coughing, often worse at night or early morning
- Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing
- Fatigue during physical activity
Severe asthma symptoms (medical emergency):
- Trouble speaking due to breathlessness
- Blue lips or fingernails
- Speedy breathing
- Little or no improvement with inhaler use
What Are The Causes of Asthma Attacks?
Asthma attacks can be caused by many triggers that vary from person to person. Common triggers include allergens, respiratory infections (such as the flu and cold), cold air, tobacco smoke, and emotional stress. It’s an essential part of asthma management to be aware of triggers and avoid them.
How is Asthma Diagnosed?
Asthma attacks are increasingly common and affect adults and children alike. Most asthma attacks can be anticipated and require spirometry and asthma history. For children, the challenge in diagnosing asthma is the overlap of symptoms and the difficulty of lung function tests. Diagnosis is often made during routine cold and flu care.
Treatment Options for Asthma
Although asthma cannot be completely cured, it can be controlled with the appropriate treatment. Asthma management focuses on preventing symptoms, reducing the risk of asthma attacks, and enabling active participation without limitations. This is the primary goal of asthma management.
Controller Medications
Controller medications are taken daily to reduce airway inflammation and symptoms. Corticosteroids are frequently prescribed and are the foundation of asthma treatment.
Additional long-term medications can be prescribed when symptoms worsen and when treatment is not as effective.

Quick-Relief Medications
Quick-relief medications, or “rescue inhalers” as they are commonly called, provide immediate symptom control for sudden symptoms by relaxing the muscles around the airways. These medications are fast-acting and critical for the management of asthma attacks.
Asthma attacks are a medical emergency and may be poorly controlled if the person frequently relies on the rescue inhalers. This may indicate a need to discuss other treatment options with a health care provider.
Lifestyle Adjustments
The Role of Environmental control measures in the management of asthma is critical. Minimizing exposure to allergens, tobacco smoke, and respiratory infections can help reduce the frequency of asthma attacks.
Regular physical activity is also encouraged to enhance overall health and maintain good lung function. This is important, though some people may need adjustments to their medications to exercise comfortably.
Asthma Action Plans
Most providers recommend using an asthma action plan, which serves as a personalized roadmap for patients and includes a routine management plan, identification of potential triggers, and recommendations for action steps in the event of an asthma attack.
Plans foster a more organized approach to asthma management, giving the patient a better chance of avoiding the ED when symptoms worsen.
Asthma in Children vs. Adults
Asthma is a disease of childhood, though it can occur at any age. Children may outgrow asthma, while adults have a more chronic disease.
Work exposures and chronic sinus disease, if present, may cause asthma symptom triggers in adults. Also, reactive airway disease may be exacerbated in women by specific endocrine changes.
Complications of Poorly Controlled Asthma
Asthma that is poorly controlled can result in an attack with emergency care, loss of lung function over time, and the development of chronic symptoms that may be due to airway remodeling as a result of chronic inflammation. Asthma attacks can be severe, life-threatening, and require emergency care at an ED.
Living Well With Asthma
Asthma can be well controlled with adequate education, ongoing involvement of a health care provider, and consistent adherence to the asthma action plan. This enables the patient to continue with a fully functional lifestyle.
Knowledge of one’s own variables, symptoms, and response therapies is essential for maintaining control of the condition.
Guidelines for When to Obtain Medical Assistance
A provider should be consulted if one has recurrent symptoms of asthma, is having an increasingly difficult time with breath control, or if the rescue medications are no longer working. Extreme difficulty with breath control, blueness of the lips and/or fingers, and difficulty with verbal expression due to breath control are indications for emergency services intervention.
Contact us if you need any medical information, guidance, or support.