Did you know that nearly 95% of Americans don’t get enough omega-3 fatty acids in their daily diet? This staggering statistic reveals a hidden health crisis affecting millions. Moreover, omega-3 deficiency contributes to inflammation, heart disease, and cognitive decline. However, the good news is that fixing this nutritional gap doesn’t require expensive supplements or drastic lifestyle changes.
Understanding omega-3 deficiency starts with recognising its widespread impact on modern health. Therefore, this comprehensive guide will reveal the secrets behind omega-3 deficiency and show you exactly how to address it through simple dietary changes.

Understanding Omega-3 Deficiency: The Hidden Health Crisis
Omega-3 fatty acids represent essential nutrients your body cannot produce on its own. Consequently, you must obtain these vital fats through food or supplements. The three main types include ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid).
Unfortunately, the typical Western diet severely lacks adequate omega-3 intake. Meanwhile, processed foods high in omega-6 fatty acids dominate our plates. This imbalance creates inflammation, setting the stage for the development of chronic diseases.
Research from the Harvard School of Public Health indicates that omega-3 deficiency is among the top dietary risk factors for mortality in America. Furthermore, inadequate intake affects brain function, heart health, and immune system performance.
Signs of Omega-3 Deficiency You Shouldn’t Ignore
Recognising the symptoms of omega-3 deficiency enables you to take action before serious health issues develop. Therefore, pay attention to these warning signs your body sends.
Physical symptoms include:
- Dry, flaky skin and brittle nails
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Frequent infections and slow wound healing
- Hair loss and dull, lifeless hair
Cognitive and emotional symptoms manifest as:
- Memory problems and difficulty concentrating
- Mood swings and increased anxiety
- Depression and irritability
- Sleep disturbances and fatigue
Additionally, cardiovascular symptoms such as high blood pressure and irregular heartbeat may indicate an omega-3 deficiency. However, these symptoms can overlap with other conditions. Therefore, consulting a healthcare provider ensures an accurate diagnosis.
At Healthabulous, we believe in empowering readers with evidence-based nutrition information to make informed decisions about their health.
What Causes Omega-3 Deficiency in Modern Diets
Several factors contribute to widespread omega-3 deficiency in today’s society. First, the standard American diet emphasises processed foods over whole, nutrient-dense options. Consequently, omega-6 fatty acids from vegetable oils overwhelm the beneficial omega-3s.
Industrial food production methods further compound this problem. For instance, grain-fed livestock produces meat with lower omega-3 content compared to grass-fed animals. Similarly, farmed fish often contain fewer omega-3s than wild-caught varieties.
Moreover, food processing destroys delicate omega-3 fatty acids through heat and chemical treatments. Therefore, packaged and prepared foods offer minimal omega-3 benefits.
Environmental factors also play a role. Pollution and overfishing reduce the omega-3 content in marine sources. Additionally, soil depletion affects the omega-3 levels in plant-based foods.
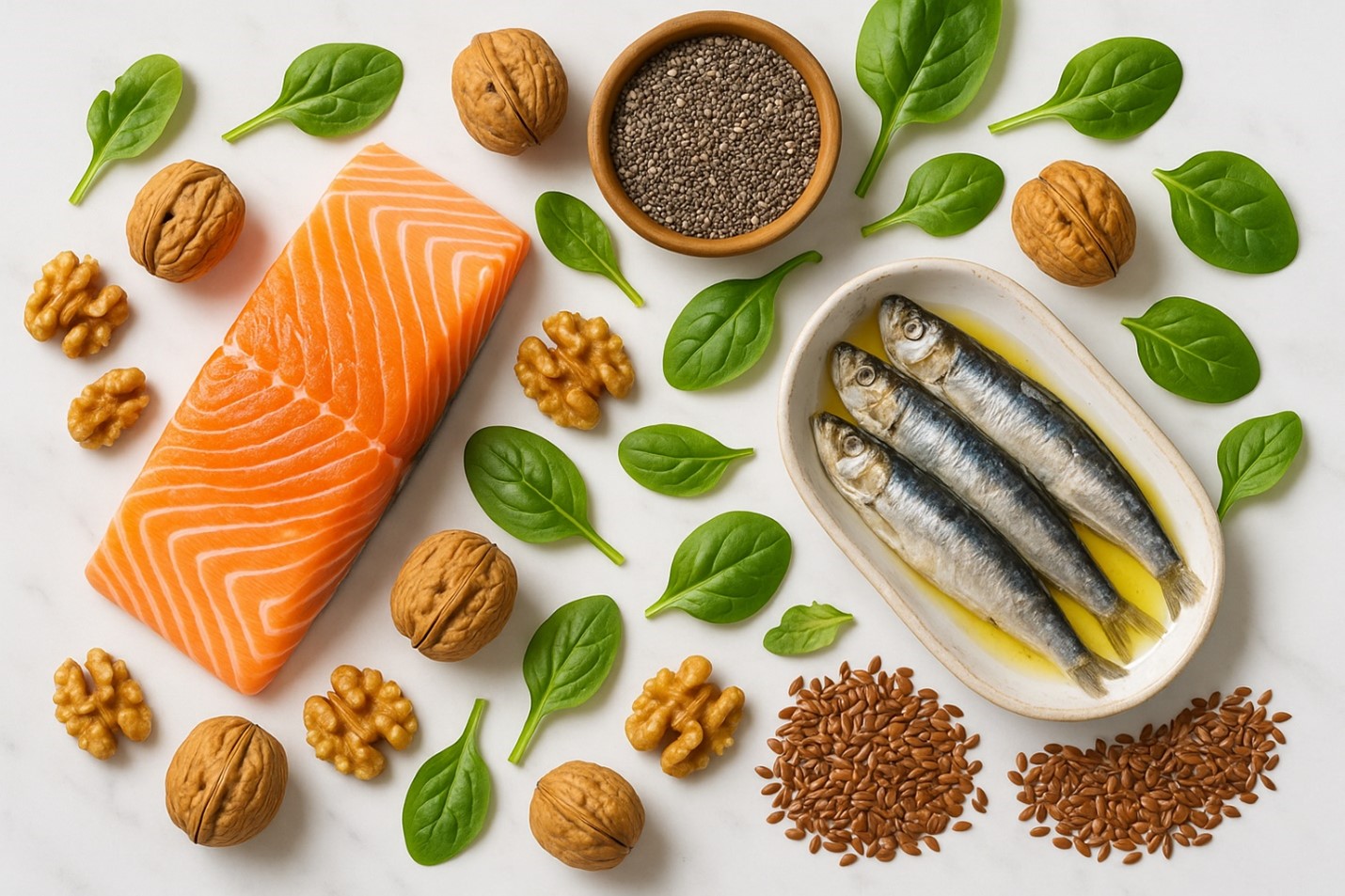
Best Omega-3 Foods for Fixing Deficiency Naturally
Addressing omega-3 deficiency through food provides the most sustainable and practical approach. However, choosing the right sources ensures optimal absorption and health benefits.
Marine Sources: The Omega-3 Powerhouses
Fatty fish delivers the highest concentrations of EPA and DHA omega-3s. Therefore, incorporating these options into your weekly meal plan provides substantial benefits:
Wild-caught salmon tops the list with approximately 1,500mg of omega-3s per 3.5-ounce serving. Meanwhile, sardines offer exceptional value with 1,400mg in the same portion size. Mackerel provides 1,100mg, and anchovies deliver 950mg per serving.
Shellfish also contribute meaningful amounts. For example, oysters contain 400mg per serving, while mussels provide 300mg. Even canned tuna offers 250mg, though fresh varieties contain higher levels.
Plant-Based Omega-3 Sources for Every Diet
Plant foods primarily contain ALA omega-3s, which the body converts to EPA and DHA. However, this conversion process is inefficient. Therefore, plant-based eaters need higher intake levels.
Flaxseeds lead plant sources with 6,400mg of ALA per ounce. Similarly, chia seeds provide 4,900 milligrams, while hemp seeds offer 2,600 milligrams per serving. Walnuts deliver 2,500mg per ounce.
Leafy greens contribute smaller but significant amounts. For instance, spinach contains 166mg per cup, and kale provides 134mg. Brussels sprouts offer 135mg of vitamin C per cup when cooked.
Fortified Foods and Oils
Certain fortified foods help bridge omega-3 gaps in modern diets. Omega-3-enriched eggs from pasture-raised hens contain 100-200mg per egg. Meanwhile, fortified milk and yoghurt offer convenient options for daily consumption.
Algae oil represents the only direct plant source of DHA omega-3 fatty acids. Therefore, vegetarians and vegans benefit significantly from this supplement alternative.
How Much Omega-3 Do You Need Daily?
Understanding daily omega-3 requirements helps optimise your intake strategy. The American Heart Association recommends specific amounts based on health status and goals.
For general health maintenance, consume 250-500mg combined EPA and DHA daily. However, individuals with heart disease benefit from 1,000mg daily under medical supervision. Meanwhile, pregnant women need at least 200mg DHA for fetal brain development.
Plant-based diets require 2,000-3,000mg ALA daily to achieve adequate EPA and DHA levels. Therefore, vegans and vegetarians should prioritise multiple ALA sources throughout the day.
Creating Your Omega-3 Rich Diet Plan
Building a sustainable omega-3 diet plan requires strategic meal planning and preparation. Therefore, start by incorporating omega-3 foods into familiar recipes and gradually expand your repertoire.
Breakfast options include chia seed pudding, walnut-topped oatmeal, or omega-3-enriched eggs. Moreover, adding ground flaxseed to smoothies provides an easy boost.
Lunch suggestions feature sardine salads, salmon bowls, or hemp seed-topped soups. Additionally, spinach and kale salads with walnut dressing maximise plant-based intake.
Dinner options include baked mackerel, grilled salmon, or plant-based meals with multiple sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Furthermore, cooking with algae oil instead of regular vegetable oils increases daily intake.

Omega-3 vs Omega-6: Achieving the Right Balance
The omega-3 to omega-6 ratio has a significant impact on inflammation and overall health. Ideally, this ratio should range from 1:1 to 1:4. However, the typical Western diet creates ratios as high as 1:20, promoting chronic inflammation.
Reducing omega-6 intake proves as necessary as increasing omega-3 consumption. Therefore, limit processed foods containing soybean, corn, and sunflower oils. Instead, choose olive oil, avocado oil, or coconut oil for cooking.
Simultaneously, emphasise whole foods over packaged alternatives. Fresh fruits, vegetables, and unprocessed proteins naturally provide better omega fatty acid profiles.
Maximising Omega-3 Absorption and Benefits
Several factors influence how effectively your body absorbs and utilises omega-3 fatty acids. Therefore, implementing these strategies maximises your dietary efforts.
Timing matters for omega-3 absorption. Consuming these fats with meals that contain other healthy fats improves their uptake. For instance, pairing salmon with avocado or nuts enhances absorption.
Food preparation also affects omega-3 content. Gentle cooking methods, such as steaming or baking, preserve delicate fatty acids better than high-heat frying. Meanwhile, storing omega-3-rich foods properly prevents rancidity.
Synergistic nutrients support omega-3 function. Vitamin E protects omega-3 fatty acids from oxidation, while vitamin D enhances their anti-inflammatory effects. Therefore, consume a varied diet rich in antioxidants and vitamins.
Common Myths About Omega-3 Deficiency
Several misconceptions surround omega-3 deficiency and supplementation. Therefore, separating fact from fiction helps make informed decisions.
Myth: All fish provide equal omega-3 benefits.
Reality: Fatty fish contain significantly more omega-3s than lean varieties like cod or tilapia.
Myth: Plant-based omega-3s work identically to marine sources.
Reality: The ALA conversion to EPA and DHA is limited, requiring higher intakes of plant-based foods.
Myth: Omega-3 supplements always work better than food sources.
Reality: Whole foods provide synergistic nutrients that enhance the absorption and function of omega-3 fatty acids.
Conclusion
Omega-3 deficiency affects millions of people worldwide; yet, simple dietary changes can help address this widespread nutritional gap. Therefore, prioritising omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts provides sustainable health benefits.
Remember that consistency matters more than perfection when building omega-3 intake. Moreover, combining multiple sources throughout the day ensures that adequate levels of these essential fatty acids are maintained.
Start incorporating these omega-3 strategies today to support heart health, brain function, and overall wellness. However, consult healthcare providers for personalised guidance, especially if you have existing health conditions or take medications. For more evidence-based nutrition guides and health tips, visit Healthabulous where we help you make informed decisions about your wellness journey.
Frequently Asked Questions About Omega-3 Deficiency
How long does it take to fix omega-3 deficiency?
Most people notice improvements in 6-12 weeks with consistent omega-3 intake. Dry skin may improve within 2-4 weeks, while cognitive benefits take 2-3 months.
Can you get too much omega-3 from food sources?
Omega-3 toxicity from food is extremely rare. However, very high intake (above 3,000mg daily) may increase bleeding risk in some individuals.
Are omega-3 supplements necessary if I eat fish regularly?
Most people can meet omega-3 needs by eating fatty fish 2-3 times weekly. Pregnant women, vegetarians, or those with health conditions may need supplements.
Which omega-3 type is most important: ALA, EPA, or DHA?
Each serves unique functions. DHA supports brain health, EPA provides anti-inflammatory benefits, and ALA converts to both EPA and DHA. Consume varied sources for optimal intake.
Do cooking methods affect omega-3 content in foods?
Yes, high-heat cooking destroys omega-3s. Use gentle methods, such as baking, steaming, or grilling at moderate temperatures, to preserve the content.